Meta Description: Discover how search engines work — from crawling and indexing to ranking. Learn SEO strategies aligned with Google’s algorithm for higher visibility in 2025.
How Search Engines Work: Crawling, Indexing, and Ranking Explained
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is a Search Engine?
- The Core Functions of a Search Engine
- 1. Crawling: Discovering New Content
- 2. Indexing: Storing and Organizing Content
- 3. Ranking: Delivering the Best Results
- How Google’s Algorithm Works in 2025
- The Role of AI and Machine Learning
- SEO and Its Relationship With Search Engines
- Common Challenges in Search Engine Optimization
- Latest Trends in Search Engines
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In the current landscape web search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo serve as pathways to online content. But how do they work behind the scenes to connect users with the most relevant results for billions of searches every day?
This guide will break down the complete process of how search engines work (crawling, indexing, ranking) – and how these processes relate to the current world of SE0 Strategies in 2025.
What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a web-based software system designed to carry out web searches. It indexes billions of web pages and delivers the most relevant results based on your query.
Popular search engines include:
- Bing
- Yahoo
- DuckDuckGo
- Yandex
- Baidu (China)
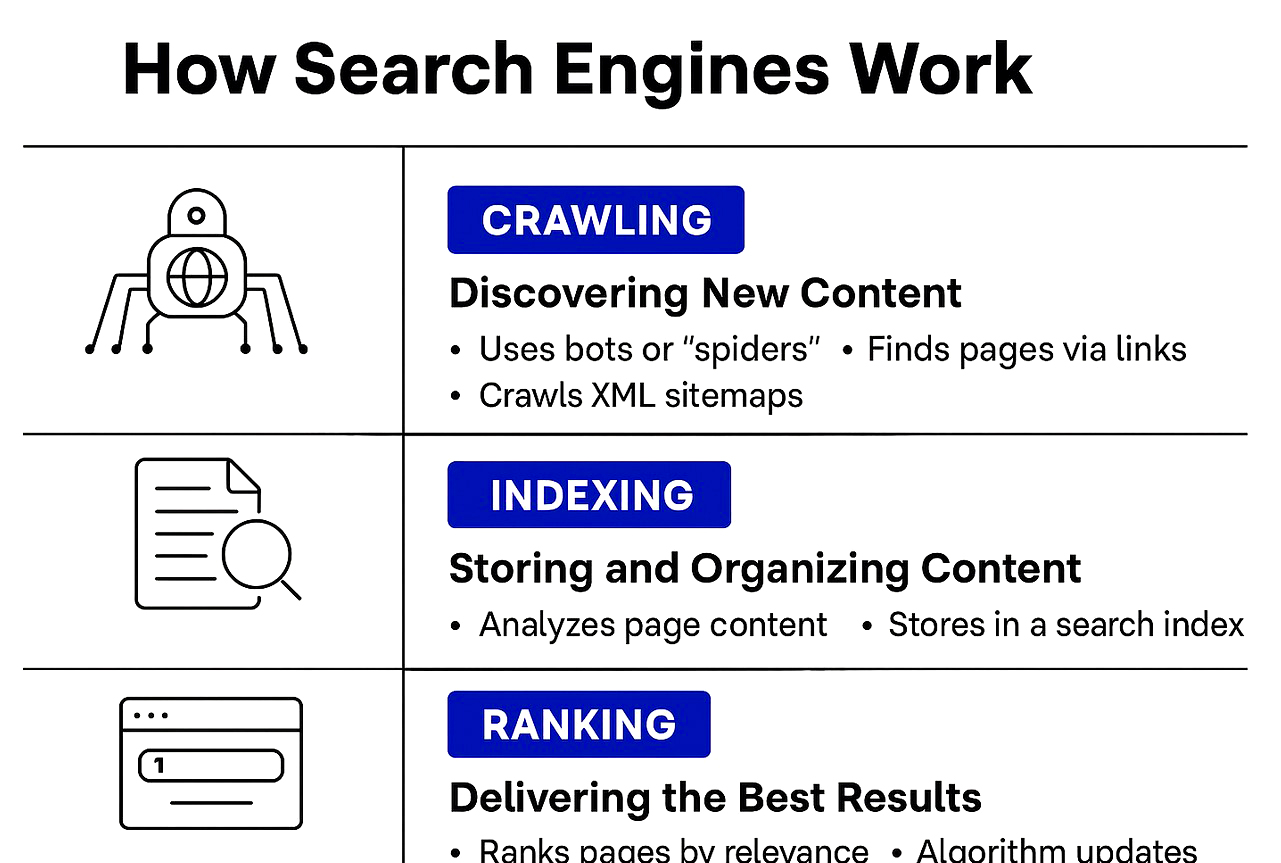
The Core Functions of a Search Engine
Search engines perform three core functions:
- Crawling – Discovering content
- Indexing – Storing and organizing the content
- Ranking – Presenting the most relevant content in response to a search
Let’s break down each step.
Crawling: Discovering New Content
Crawling is the process by which search engines scan the internet to find new and updated content. This includes web pages, images, videos, PDFs, etc.
How It Works:
- Search engines use bots or spiders (e.g., Googlebot).
- These bots follow links from page to page.
- XML sitemaps help bots discover URLs efficiently.
Key Tools:
- Robots.txt – A file to instruct bots what they can/can’t crawl.
- Sitemaps – A map of your site’s important pages.
Crawling is the first step in the search engine process. If your website isn’t crawled, it won’t appear in search results.
Indexing: Storing and Organizing Content
Once crawled, the content goes through indexing. This is when search engines analyze and store the page in a massive database.
What Gets Indexed:
- Page content (text, headings)
- Keywords
- Metadata (title, description)
- Images (with alt tags)
- Internal and external links
Tips for Better Indexing:
- Use clear, keyword-rich headings
- Avoid duplicate content
- Ensure mobile-friendliness
- Implement structured data (schema markup)
Search engines must understand the context of your content to index it correctly.
Ranking: Delivering the Best Results
Ranking is the most competitive and crucial part of the process. After crawling and indexing, search engines decide which content should appear at the top of search results.
Ranking Factors:
- Relevance to the query
- Content quality
- User experience (UX)
- Page speed
- Mobile optimization
- Backlinks (quality over quantity)
- Domain authority
- Engagement metrics (bounce rate, time on site)
In 2025, Google uses over 200 ranking signals powered by machine learning.
How Google’s Algorithm Works in 2025
Google’s ranking algorithm has evolved to prioritize user intent and experience using AI technologies like:
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)
- MUM (Multitask Unified Model)
- RankBrain
These models help Google understand:
- Natural language queries
- Context of content
- Search intent
So instead of matching keywords blindly, Google focuses on semantic relevance.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Search engines now heavily rely on AI to:
- Interpret long-tail or conversational queries
- Detect spam and thin content
- Personalize search results
- Optimize featured snippets, “People also ask,” etc.
In 2025, machine learning plays a central role in ranking and refining results continuously.
SEO and Its Relationship With Search Engines
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the practice of aligning your content with the mechanics of search engines to improve visibility.
On-Page SEO:
- Optimizing headings, meta tags, and keywords
- Using proper image alt attributes
- Creating quality, useful content
Off-Page SEO:
- Gaining high-authority backlinks
- Building social signals
- Online reputation management
Technical SEO:
- XML sitemaps
- Mobile responsiveness
- Site speed improvements
- Structured data markup
SEO works in harmony with how search engines crawl, index, and rank content.
Common Challenges in Search Engine Optimization
- Duplicate content
- Index bloat (too many unnecessary pages indexed)
- Low-quality backlinks
- Content not ranking despite being crawled
- Penalty from algorithm updates
Keeping up with Google’s updates and guidelines is key to overcoming these challenges.
Latest Trends in Search Engines
- Voice Search Optimization: Targeting conversational keywords.
- Core Web Vitals: UX metrics that affect rankings.
- AI-generated Content: Needs human optimization.
- Zero-Click Searches: Featured snippets and knowledge panels.
- Visual Search: Image-based queries gaining popularity.
Search engine algorithms are now more about intent, context, and experience than just keywords.
Conclusion
For anyone creating a digital asset in 2025, understanding how search engines operate is a prerequisite.
From crawling your content, to storing it away in enormous databases, to serving up results based on different sources of signals, search engines are now intelligent, AI-based systems.
To distinguish yourself from other search results:
• Figure out how to provide quality, well-organized content.
• Optimize your content for both users and bots.
• Monitor, to some degree, the trending algorithms.
By tailoring your SEO tactics to the workings of search engines, you prepare your content to rise to the top where visibility means success.
FAQs
How do search engines crawl websites?
Search engines employ bots (such as Googlebot) to follow links and read pages. The bots start with a list of known URLs and may use sitemaps.
What is the difference between indexing and ranking?
Indexing simply means storing information about a page. Ranking involves how that page eventually shows up in the search results, based on how relevant and authoritative it is.
How often does Google update its algorithm?
Google will update its algorithm thousands of times a year, but large core updates will frequently roll out every few months.
What is a search engine algorithm?
A search engine algorithm is a set of rules and guidelines search engines use to determine the ranking and placement of your content on the search results page. The search engine algorithm looks for things like relevance, user intent, authoritativeness, and the performance of the site.
Why isn’t my page showing up on Google?
You may have not been crawled yet by a bot, you may have been crawled but not indexed, it may have been blocked by robots.txt, you provided poor content, or you have been penalized for spammy SEO practices.
Can I control how and when my site is indexed?
In a sense, you can manage how or if content is indexed with robots.txt, noindex meta tags, and canonical tags.
Google SEO Keywords: how search engines work, search engine algorithms, crawling indexing ranking, SEO and search engines, Google algorithm explained, how does Google rank websites, how does search engine indexing work, search engine ranking process, search engine crawling, what is a search engine crawler
![]()

[…] change, real value, an honest user experience, and a commitment to learning about Google and other search engines‘ algorithms is paramount. As a beginner or a seasoned expert, once you have developed a […]
[…] promoting products or services via the internet and digital platforms. This can include the use of search engines, websites, social media, email, and mobile apps as marketing channels to help businesses reach a […]