META DESCRIPTION: Understand the CPI report and the Consumer Price Index. Learn how CPI is calculated, its impact on inflation, interest rates, and the economy. Full guide with examples.
CPI Report | Understanding the Consumer Price Index & Its Economic Impact
Table of Contents
- What Is the CPI?
- How the CPI Is Calculated
- Why the CPI Matters
- How CPI Affects Inflation
- CPI and Interest Rates
- Interpreting the CPI Report
- CPI vs Core CPI
- Impact of CPI on Households and Businesses
- The CPI and the Federal Reserve
- Historical Trends in CPI
- Recent CPI Reports (2024–2025 Snapshot)
- Global CPI Comparison
- Limitations of the CPI
- Alternatives to CPI
- Conclusion: Why You Should Monitor CPI Data
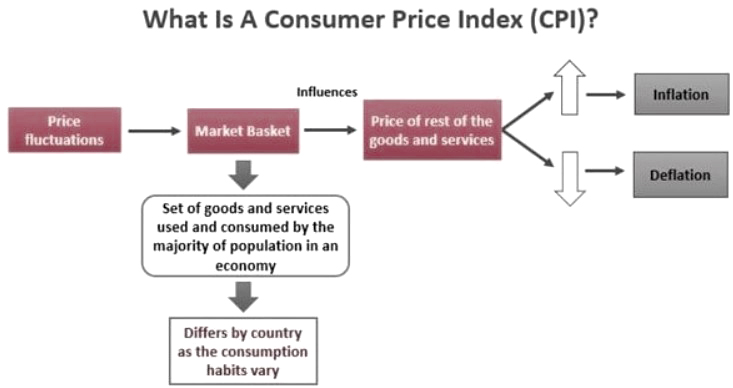
What Is the CPI?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is one of the most recognized indicators of inflation. The CPI tracks the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of goods and services. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) publishes the CPI every month, making it one of the most important indicators of economic health.
How the CPI Is Calculated
CPI is based on a weighted basket of categories that encompass:
• Food and beverages
• Housing
• Apparel
• Transportation
• Medical care
• Recreation
• Education and communication
Each category is given a weight, which demonstrates its relative significance in the contribution of each good/service or category of goods/services, in terms of total consumer expenditure. Prices are collected across the U.S. and are then compared against a base year to arrive at an index.
Formula:
CPI = (Cost of basket in current year / Cost of basket in base year) × 100
Why the CPI Matters
The CPI is more than a number. It:
- Tracks the cost of living
- Helps in adjusting salaries, pensions, and tax brackets
- Affects financial markets and investment strategies
- Guides monetary policy decisions
How CPI Affects Inflation
Inflation occurs when the general level of prices rises. A rising CPI typically indicates increasing inflation, while a declining CPI might signal deflation or slowing inflation.
Types of CPI Movements:
- Disinflation: Slowing rate of inflation
- Hyperinflation: Extremely high inflation rates
- Deflation: General decline in prices
CPI and Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve closely monitors CPI data. If CPI rises rapidly, the Fed may increase interest rates to cool demand. Conversely, a low CPI could result in rate cuts to stimulate growth.
CPI directly impacts:
- Mortgage rates
- Credit card interest rates
- Bond yields
- Currency strength
Interpreting the CPI Report
The monthly CPI report includes:
- Headline CPI: All items including food and energy
- Core CPI: Excludes food and energy due to their volatility
- Month-over-month (MoM) and year-over-year (YoY) percentage changes
Example:
CPI rose 0.4% MoM in April and 3.2% YoY, signaling persistent but moderating inflation.
CPI vs Core CPI
While headline CPI reflects total inflation, core CPI provides a clearer picture of underlying inflation trends, which is why it’s the Fed’s preferred measure for long-term policy analysis.
Impact of CPI on Households and Businesses
For Consumers:
- Affects purchasing power
- Influences wage negotiations
- Impacts rent, groceries, and utility bills
For Businesses:
- Changes in input costs
- Impacts pricing strategies
- Influences supply chain planning and wage costs
The CPI and the Federal Reserve
The Fed uses CPI (alongside PCE) to:
- Set inflation targets (2%)
- Adjust interest rates
- Plan quantitative tightening or easing
A consistently high CPI could lead to hawkish policies, while a low CPI may trigger dovish actions.
Historical Trends in CPI
From the 1970s stagflation era to the hyperinflation scare of the early 2020s, CPI trends have shaped monetary history.
Key historical highlights:
- 1980: CPI peaked at 13.5%
- 2008: Sharp spike before global crisis
- 2022: Highest YoY CPI since 1981 (9.1%)
Recent CPI Reports (2024–2025 Snapshot)
Here’s a look at some of the recent CPI reports:
| Month | CPI YoY | Core CPI YoY | Trend |
| Jan 2025 | 3.1% | 3.4% | Slight decline |
| Feb 2025 | 3.3% | 3.6% | Sticky inflation |
| Mar 2025 | 3.2% | 3.5% | Flat |
| Apr 2025 | 3.2% | 3.4% | Mixed signals |
Market reactions have been cautious, with equities and bonds responding sharply to any surprises.
Global CPI Comparison
Different countries have different CPI structures, but the concept remains similar.
| Country | Latest CPI (YoY) | Notes |
| USA | 3.2% | Moderate inflation post-peak |
| UK | 3.9% | Energy-driven pressures |
| EU (Eurozone) | 2.6% | Near ECB target |
| Japan | 2.1% | Recently exiting deflation cycle |
Global CPI trends impact currency markets, trade flows, and geopolitical stability.
Limitations of the CPI
CPI is not a perfect measure. Key criticisms include:
- Doesn’t capture regional variations
- May overestimate or underestimate cost of living
- Excludes asset inflation (like housing prices or stocks)
- Uses fixed baskets that don’t account for changing consumer habits
Alternatives to CPI
Other inflation measures include:
- PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures) – preferred by the Fed
- GDP deflator – broader economic scope
- Core PPI (Producer Price Index) – upstream price trends
Conclusion: Why You Should Monitor CPI Data
So Why Monitor CPI Data? The CPI report is an important economic indicator that influences almost every aspect of daily life from grocery store prices to how mortgage rates are determined. It matters to investors, economists, and policy makers who refer to the CPI monthly report to determine inflation trends, interest rate outlook, and financial planning decisions.
Understanding CPI is necessary to make educated financial decisions, anticipate potential market changes, and assess the health of the economy. With inflation being a primary concern worldwide, it is never more important to monitor CPI.
SEO Keywords: CPI report, Consumer Price Index, what is CPI, CPI inflation data, CPI and interest rates, US inflation report, CPI explained, economic indicators, monthly CPI data, inflation vs CPI, CPI news today, CPI trend analysis, Federal Reserve CPI, inflation report explained
![]()

